Vdip2 - Fault Localization on MV Using Measurements on the LV Side in Distribution Transformer Stations
The localization of ground faults in compensated MV networks remains one of the challenges awaiting a precise and effective solution. Currently used methods are based on fault passage indicators integrated into remotely controlled sectionalizers/breakers or manual/portable fault passage indicators that evaluate the electromagnetic field of overhead lines before and after the fault – both methods are available in the ELVAC portfolio. However, multiple reclosures of the feeder to the ground connection may still be necessary during the localization process.
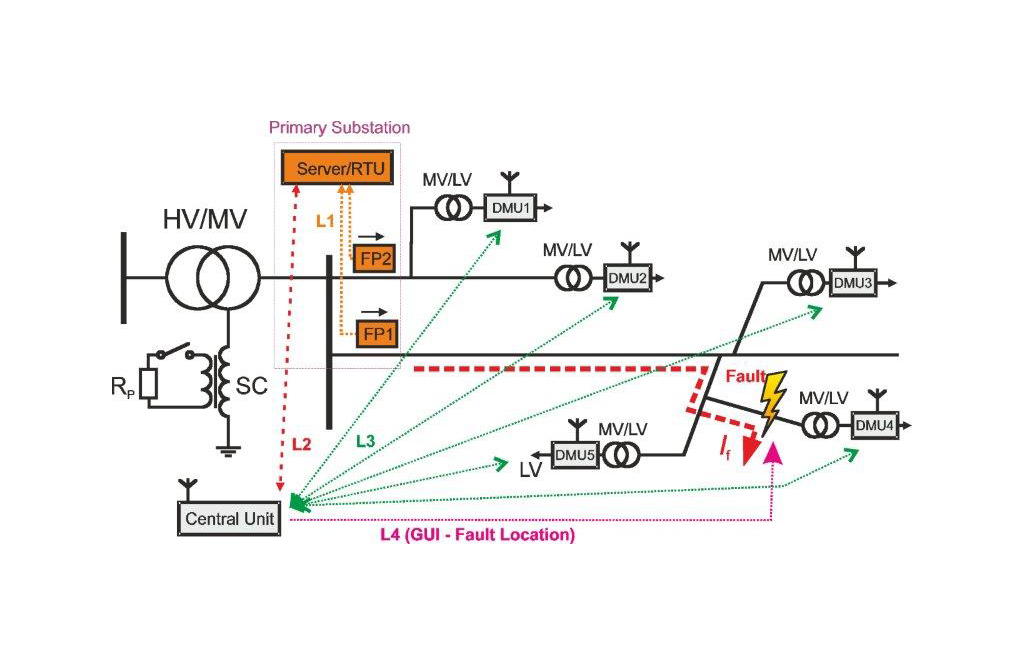
We present an alternative method called “Vdip2” (Vdip 2nd generation), which utilizes distributed measuring units (DMUs) placed on the secondary sides of MV/LV distribution transformers. Based on the data collected from these units, the system is then able to calculate the most likely fault location and display it on a map (GIS), or transfer it to other systems (SCADA). In addition to the localization of ground faults, which is the primary benefit, the system also determines the location and type of short circuits. The modular concept of the software solution allows for easy integration with other analytical and statistical tools to maximize the use of data obtained from measuring and control systems in the field and substations, with the aim of improving the operation of distribution networks, increasing their availability, reliability, and safety.
Vdip2 system description
The Vdip2 system was designed for the automatic localization of ground faults in compensated (resonantly grounded) systems, which are difficult to locate due to the low level of ground fault currents. Due to its functional principle, the Vdip2 system can also be used for fault localization in short-circuit events.
The Vdip monitoring system consists of feeder protection units (FP) and distributed measuring units (DMU), which are located on the secondary side of the HV/LV transformers. In the event of a fault, the feeder protection is triggered, generating a fault record that is immediately transmitted to a concentrator (PC or RTU) located at the primary HV/HV substation and subsequently to the central unit of the Vdip2 system (server). The fault indication from the feeder protection also initiates the download of records from the moment the fault occurs, from individual DMUs located at transformer stations connected to the affected feeder.
The Vdip2 system can incorporate any voltage monitor that allows storing phase voltage oscillograms in a circular buffer and sending a fault record for the specific moment of fault occurrence. ELVAC also offers suitable and cost-effective devices (RTU and low-voltage monitors) that complement the complete solution, so the selection depends on the customer and their initial conditions (existing devices in the network).
Fault records from DMU and FP units are synchronized and processed in the central unit to obtain changes in the negative sequence voltage ΔUm(2) and current ΔIm(2), which are inputs to the Vdip2 localization algorithm. The entire process is extended for practical deployment with complex preprocessing of input data, and the results from the localization algorithm are then internally evaluated and aggregated to improve the reliability and accuracy of the presented result.
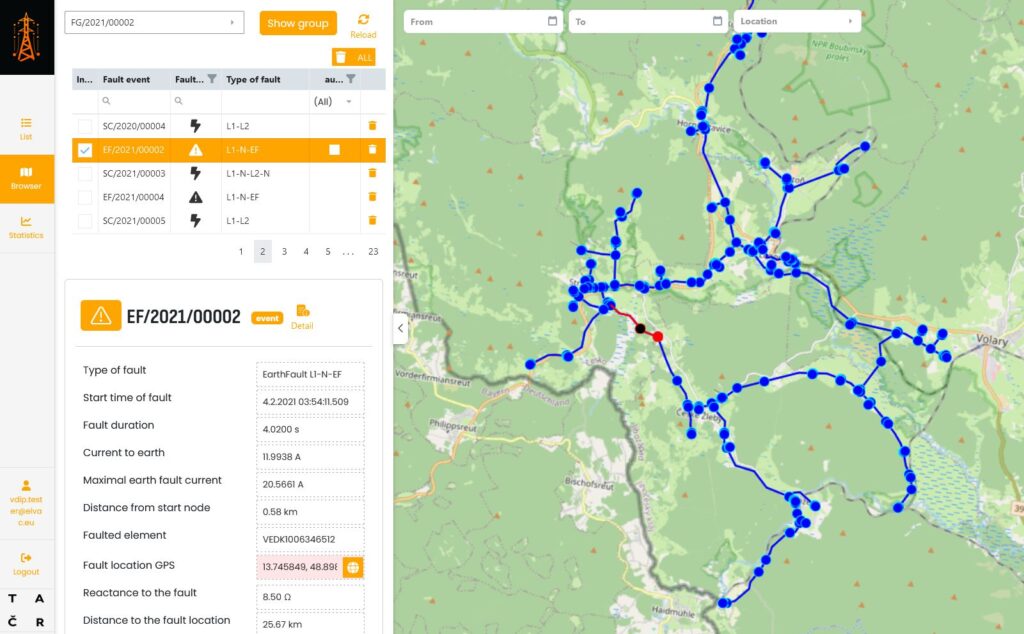
The localization algorithm of the Vdip2 system is based on a patented method, where the current reverse sequence monitor (MZSP) represents the respective feeder protection, and the voltage reverse sequence monitors (MZSN) represent the individual DMUs. The result of the localization algorithm is the identification of a specific node in the network and the distance from this node to the fault location, with the system also capable of determining the exact coordinates of the expected fault location using GIS data. The results are displayed to the dispatchers via a graphical user interface (part of the software solution, but integration into existing SCADA or OMS systems is also possible).
An advantage of the Vdip2 system is the ability to perform multiple fault localizations based on a single set of fault records. The reliability of the identified fault location can then be assessed based on the deviation of fault locations obtained from one set of records.
More detailed information can be found in the following documents:
Presentation of the Vdip2 system web interface
Components and Licensing of the System
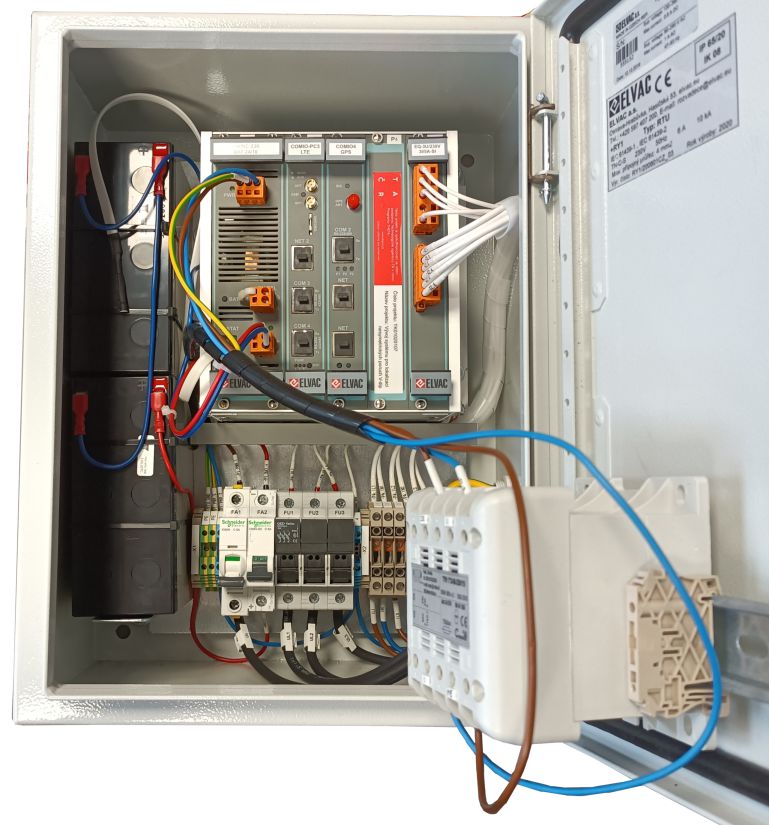
It is possible to purchase a DMU assembly based on the RTU7M unit from ELVAC, which integrates a low-voltage monitor (voltage quality analyzer) and a communication module (via an LTE modem or other standards). If suitable voltage monitoring devices are already installed in the network, the RTU7MC3 communication device from ELVAC can be used to manage the connection and data transfer to the Vdip system server. It is also possible to implement all required functions into third-party devices.
The licensing of the Vdip2 system is based on a base license, feeder licenses, and licenses for DMU devices, which are “vendor-independent” and managed by the Vdip2 system server. The Vdip2 software provides a web interface for regular users, an administrative tool (Windows application) for system configuration and maintenance, and also an integration API for connecting with other software systems used by the network operator.